[자료구조] 배열을 이용한 다항식 표현1
- -
배열을 이용한 다항식 표현
다항식의 일반적인 형태는 다음과 같습니다.
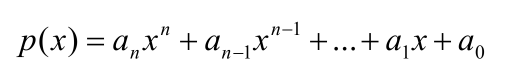
프로그램에서 다항식을 처리하려면 다항식을 위한 자료구조가 필요합니다.
배열을 이용한 다항식의 표현 방법에는 2가지가 있습니다.
>> (1) 모든 항을 저장한다.
>> (2) 0이 아닌 항만을 저장한다.
(1) 모든 항을 저장하는 방식
#define MAX_DEGREE 101 // (다항식의 최대차수 + 1) 101
#include <stdio.h>
typedef struct {
int degree; //최고차항의 지수
float coef[MAX_DEGREE];
}polynomial;
polynomial a = { 5,{10,0,0,0,6,3} }; //10X^5+6X+3
polynomial poly_add1(polynomial A, polynomial B)
{
polynomial C; //A와 B를 더한 결과 다항식
int Apos = 0, Bpos = 0, Cpos = 0;
int degree_a = A.degree; //A다항식의 최고차항의 지수
int degree_b = B.degree; //B다항식의 최고차항의 지수
C.degree = MAX(A.degree, B.degree); // A와 B의 지수 중 더 큰 값
while (Apos <= A.degree && Bpos <= B.degree) {
if (degree_a > degree_b) { //A항 지수 > B항 지수
C.coef[Cpos++] = A.coef[Apos++];
degree_a--;
}
else if (degree_a == degree_b) { //A항 지수 = B항 지수
C.coef[Cpos++] = A.coef[Apos++] + B.coef[Bpos++];
degree_a--;
degree_b--;
}
else (degree_a < degree_b) { //A항 지수 < B항 지수
C.coef[Cpos++] = B.coef[Bpos++];
degree_b--;
}
}
return C;
}
void print_poly(polynomial p)
{
for (int i = p.degree; i > 0; i--)
printf("%3.1fX^%d + ", p.coef[p.degree - i], i);
printf("%3.1f\n", p.coef[p.degree]); // 마지막 상수항 출력
}
int main()
{
polynomial a = { 5,{ 2, 9, 0, 3, 0, 8 } };
polynomial b = { 4,{ 1, 0, 0, 4, 5 } };
polynomial c;
print_poly(a);
print_poly(b);
c = poly_add1(a, b);
printf("--------------------------------------------------------\n");
print_poly(c);
return 0;
}
(2) 0이 아닌 항만을 저장하는 방식
#define MAX_TERMS 101
#include <stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
struct {
float coef; // 계수
int expon; // 지수(차수)
} terms[MAX_TERMS] = { {8,3}, {7,1}, {1,0}, {10,3}, {3,2},{1,0} };
int avail = 6;
// 두 개의 정수를 비교
char compare(int a, int b)
{
if (a > b) return '>';
else if (a == b) return '=';
else return '<';
}
// 새로운 항을 다항식에 추가한다.
void attach(float coef, int expon)
{
if (avail > MAX_TERMS) {
fprintf(stderr, "항의 개수가 너무 많습니다.\n");
exit(1);
}
terms[avail].coef = coef;
terms[avail++].expon = expon;
}
// C = A + B
void poly_add2(int As, int Ae, int Bs, int Be, int* Cs, int* Ce)
{
float tempcoef;
*Cs = avail;
while (As <= Ae && Bs <= Be)
switch (compare(terms[As].expon, terms[Bs].expon)) {
case '>': // A의 차수 > B의 차수
attach(terms[As].coef, terms[As].expon);
As++;
break;
case '=': // A의 차수 == B의 차수
tempcoef = terms[As].coef + terms[Bs].coef;
if (tempcoef)
attach(tempcoef, terms[As].expon);
As++;
Bs++;
break;
case '<': // A의 차수 < B의 차수
attach(terms[Bs].coef, terms[Bs].expon);
Bs++;
break;
}
// A의 나머지 항들을 이동
for (; As <= Ae; As++)
attach(terms[As].coef, terms[As].expon);
// B의 나머지 항들을 이동
for (; Bs <= Be; Bs++)
attach(terms[Bs].coef, terms[Bs].expon);
*Ce = avail - 1;
}
void print_poly(int s, int e)
{
for (int i = s; i < e; i++)
printf("%3.1fx^%d + ", terms[i].coef, terms[i].expon);
printf("%3.1fx^%d\n", terms[e].coef, terms[e].expon); //마지막 상수항 출력
}
int main()
{
int As = 0, Ae = 2, Bs = 3, Be = 5, Cs, Ce;
poly_add2(As, Ae, Bs, Be, &Cs, &Ce);
print_poly(As, Ae);
print_poly(Bs, Be);
printf("----------------------------------------------------------------------------- \n");
print_poly(Cs, Ce);
return 0;
}
위 두 가지 방식에서 계수를 읽는 함수와 특정 x값에서 다항식의 결괏값을 만들어내는 함수를 만들어볼 수 있습니다.
문제를 먼저 풀어보시고 풀이를 확인해보시기 바랍니다.
문제 :: 모든 항을 저장하는 방식
1-1. 차수t 에서 계수를 읽는 함수 coefficient() 를 작성하라
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
const int max_degree = 101;
struct polynomial {
int degree;
float coef[max_degree];
};
float coefficient(polynomial p, int t) {
float result = p.coef[p.degree - t];
cout << result << endl;
return result;
}
int main() {
polynomial p1 = { 5, {7, 4, 2, 0, 3, 9} };
coefficient(p1, 5);
coefficient(p1, 3);
return 0;
}
함수 설명
>> 지정한 차수의 계수를 찾기 위해서는 다항식 p의 계수 배열의 인덱스를 앞에서부터 찾아야 하므로 p의 전체 차수에서 t만큼 빼면 원하는 차수의 계수를 찾아낼 수 있다.
[실행결과]
다항식 7x^5 + 4x^4 + 2x^3 + 0x^2 + 3x^1 + 9x^0 에서
5차항의 계수 : 7
3차항의 계수 : 2
1-2. 특정한 x값에서 다항식의 값을 계산하는 함수 eval_poly()를 작성하라
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
const int max_degree = 101;
struct polynomial {
int degree;
float coef[max_degree];
};
float eval_poly(polynomial p, int x) {
float result = 0;
for (int i = 0; i <= p.degree; i++) {
float degree_sum = 1;
for (int j = 0; j < p.degree - i; j++) {
degree_sum *= x;
}
result += p.coef[i] * degree_sum;
}
return result;
}
int main() {
// 7x^5 + 4x^4 + 2x^3 + 0x^2 + 3x^1 + 9x^0
polynomial p2 = { 5, {7, 4, 2, 0, 3, 9} };
cout << eval_poly(p2, 2) << endl;
return 0;
}
함수설명
>> x의 거듭 제곱을 하나의 함수에서 구현하기 위해 다중 반복문을 사용해서 안쪽 반복문에서는 매 반복마다 해당 차수만큼의 x를 거듭 제곱한 결과값(degree_sum)을 별도로 저장하고 바깥 반복문에서 결과값 result에 매 반복마다 p의 계수에 degree_sum을 곱한 값을 저장하였다.
*거듭제곱을 계산하는 부분은 cmath라이브러리의 pow() 함수를 이용해도 됩니다.
[실행결과] x가 2일때, 7x^5 + 4x^4 + 2x^3 + 0x^2 + 3x^1 + 9x^0 == 319
문제 :: 0이 아닌 항만을 저장하는 방식
2-1. 차수t 에서 계수를 읽는 함수 coefficient2()를 작성하라
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
const int max_terms = 101;
struct {
float coef;
int expon;
} terms[max_terms] =
{ {14,3}, {5,1}, {2,0}, {11,3}, {9,2},{4,0} };
float coefficient2(int s, int e, int t) {
float result = 0;
for (int i = s; i <= e; i++) {
if (terms[i].expon == t)
result += terms[i].coef;
}
return result;
}
int main(void) {
int As = 0, Ae = 2, Bs = 3, Be = 5;
cout << coefficient2(As, Ae, 3) << endl;
cout << coefficient2(As, Ae, 2) << endl;
cout << coefficient2(As, Ae, 1) << endl;
cout << coefficient2(As, Ae, 0) << endl;
return 0;
}
함수설명
>> result값을 0으로 초기화하고 매개변수로 들어온 인덱스 값 s부터 e까지 반복하면서 차수가 t와 같다면 현재 인덱스의 계수를 result값에 넣는다. result값을 반환하고 만약 계수가 0인 차수가 있다면 그대로 0을 반환하도록 한다.
[실행결과] A다항식 14x^3 + 5x^1 + 2x^0 의 As와 Ae를 보내고 3차, 2차, 1차, 0차의 계수를 확인해본다.
2-2. 특정한 x값에서 다항식의 값을 계산하는 함수 eval_poly()를 작성하라
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
const int max_terms = 101;
struct {
float coef;
int expon;
} terms[max_terms] =
{ {14,3}, {5,1}, {2,0}, {11,3}, {9,2},{4,0} };
double eval_poly(int s, int e, int x) {
double result = 0;
for (int i = s; i <= e; i++) {
double expon_sum = 1;
for (int j = 0; j < terms[i].expon; j++) {
expon_sum *= x;
}
result += terms[i].coef * expon_sum;
}
return result;
}
int main()
{
int As = 0, Ae = 2, Bs = 3, Be = 5;
cout << eval_poly(As, Ae, 8) << endl;
cout << eval_poly(Bs, Be, 6) << endl;
return 0;
}
함수설명
>> x의 거듭 제곱을 하나의 함수에서 구현하기 위해 다중 반복문을 사용해서 안쪽 반복문에서는 매 반복마다 해당 차수만큼의 x를 거듭 제곱한 결과값(expon_sum)을 별도로 저장하고 바깥 반복문에서는 지정한 다항식의 인덱스 s부터 e까지 반복하면서 결과값 result에 매 반복마다 terms의 계수에 expon_sum을 곱한 값을 저장하였다. 이후 result를 반환한다.
*거듭제곱을 계산하는 부분은 cmath라이브러리의 pow() 함수를 이용해도 됩니다.
[실행결과]
x가 8일때, A 다항식 14x^3 + 5x^1 + 2x^0 = 7210
x가 6일때, B 다항식 11x^3 + 9x^2 + 4x^0 = 2704
'컴퓨터공학 💻 > 자료구조' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [자료구조] 배열을 이용한 다항식 표현2 : 행렬 (0) | 2021.04.10 |
|---|---|
| [자료구조] 함수의 매개변수로 포인터 전달 (0) | 2021.04.10 |
| [자료구조] 배열과 구조체의 활용 (0) | 2021.03.19 |
| [자료구조] 순환 알고리즘과 반복 알고리즘 비교 (0) | 2021.03.19 |
| [자료구조] 순환 알고리즘 원리 (0) | 2021.03.13 |
소중한 공감 감사합니다